RGB++ Protocol
What is RGB++?
RGB++ is an extended version of the RGB protocol that uses single-use seals and client-side validation techniques to manage state changes and transaction verification. It maps Bitcoin's UTXO set to Nervos CKB's Cells via isomorphic bindings, leveraging scripting constraints on both chains to ensure the correctness of state computation and the validity of ownership changes.
Addressing several technical limitations in the original RGB protocol, RGB++ unlocks a wide array of new capabilities, including client-side validation, transaction folding, shared state across contracts, non-interactive transfers, and more. It introduces scalable, Turing-complete smart contract functionality to Bitcoin — without requiring cross-chain transactions and without compromising on security.
Single-Use Seals
The concept of single-use seals was first introduced by Peter Todd in July, 2016. It allows for a lock of an electronic seal on a message, ensuring that the message can only be used once. Specifically, Bitcoin’s Unspent Transaction Outputs (UTXOs) can server as seals for messages, and the Bitcoin system’s consensus mechanism ensures that these UTXOs can only be spent once, meaning that these seals can only be opened once.
The RGB protocol uses single-use seals, which is based on Bitcoin UTXOs, to map RGB state changes to Bitcoin UTXOs ownership. This allows the Bitcoin system to guarantee ownership of the RGB state, as well as traceability of all state changes through the UTXO history. With single-use seals, the RGB protocol inherits Bitcoin's double spending protection and transaction traceability, both enforced by Bitcoin's consensus mechanism.
Client-Side Validation
The RGB protocol contains user state that cannot be directly verified by the Bitcoin consensus. This requires users to utilize off-chain computation to validate that RGB state changes meet expectations. Client-side validation enables users to only validate the relevant UTXO branch history, rather than irrelevant ones. RGB ‘s state security is provided through client-side validation without reliance on any centralized third party.
Problem of the RGB Protocol
The original RGB protocol introduced an innovative model: smart contracts anchored to Bitcoin’s UTXOs and validated entirely on the client side. However, it faced several practical challenges in real-world usage:
- Data Availability (DA): Users needed to retain full historical data to prove ownership, which made light clients difficult to build.
- P2P Dependency: Transaction propagation relied on an independent P2P network, requiring users to coordinate directly (e.g., recipients providing receipts).
- Immature Virtual Machine: RGB’s use of AluVM lacked toolchain support and production readiness.
- Limited Shared State: The RGB protocol lacks a reliable way to manage shared state across unhosted contracts—contracts that are not controlled by a centralized party or signer, making it difficult to support multi-party applications like DEXs, DAOs, or collaborative protocols.
Key Features of RGB++
Isomorphic Binding
RGB++ introduces isomorphic bindings between Bitcoin UTXOs and Nervos CKB Cells to overcome key limitations of the original RGB protocol. In RGB, UTXOs determine ownership, while off-chain commitments and single-use seals manage state. RGB++ maps each Bitcoin UTXO to a CKB Cell, synchronizing ownership through Bitcoin’s locking Scripts while managing state directly via the data and type fields of the CKB Cell. This design enables verifiable state transitions with on-chain support and composability.
Blockchain-Enhanced Client-Side Validation
Each RGB++ transaction results in a pair of synchronized transactions—one on Bitcoin and one on CKB. While the Bitcoin-side transaction remains compatible with the RGB protocol, the corresponding CKB transaction provides a verifiable state anchor that replaces the need for full client-side validation.
Users can choose to:
- Validate transactions by inspecting the associated CKB transaction directly, or
- Perform traditional client-side validation using local Bitcoin UTXO history.
In some advanced cases (e.g., transaction folding), lightweight access to CKB block headers is still needed to prevent double-spending. This hybrid model preserves the flexibility of client-side validation while enhancing it with a scalable, on-chain alternative.
Use Cases
Airdrop
Given a list of addresses and corresponding amounts, we can implement a complete airdrop application using RGB++. Assuming that both the pending airdrop data and the claimed address list are stored in Cell data as SMT, users can easily collect airdrops from their own addresses.
DEX & AMM
RGB++ optimizes the UTXO structure, facilitating seamless support for UTXO-based asset exchange protocols without the need for intermediaries. Additionally, RGB++ adopts a grid trading design to enhance its Automated Market Maker (AMM) model. In comparison to Uniswap's AMM model, the grid trading model offers enhanced customization and suitability for trading UTXO-based assets.
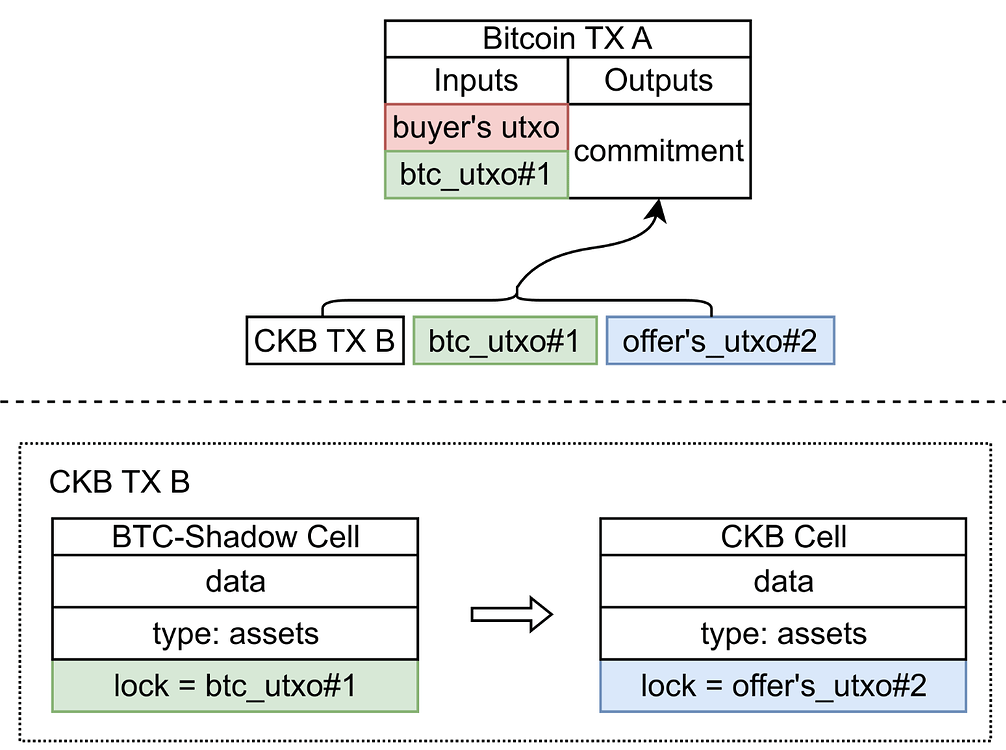
The example above illustrates a scenario where a buyer is executing a purchase using $BTC in response to a seller's pending order for RGB++ xUDT. As the transaction structure involves the buyer's UTXO, containing sufficient amount of $BTC and a PBST signature, the buyer can create a CKB transaction that meets the seller’s requirements. Afterwards, the buyer sends this signed CKB transaction to the seller. The seller then submits the BTC transaction and CKB transaction on-chain, one after the other, to complete the trade.